SalesSolution to present unique engineering solutions at the “Metal-Expo 2024” exhibition
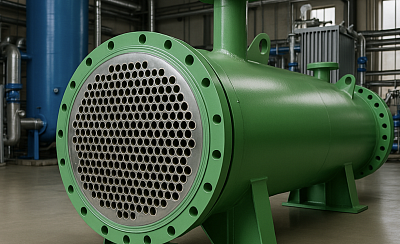
From October 29 to November 1, the Metal-Expo 2024 — the leading international exhibition for the metallurgical industry — will take place at the Expocentre in Moscow. This year, more than 500 manufacturers will showcase their products, including the largest players from the Russian and international markets. Among the exhibitors is SalesSolution, participating for the second consecutive year. SalesSolution will present its solutions for high-tech industries in Pavilion No. 2. Among them: Duplex and super duplex pipes, offering exceptional resistance to corrosion and wear, in high demand across the oil & gas sector and aggressive industrial environments Nickel alloy components, designed to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosion, especially relevant in the chemical and energy industries Large-size forgings for mechanical engineering, weighing over 10 tons — a product with virtually no market equivalents, in high demand in heavy industry Pressure vessels manufactured to international standards, used in large-scale industrial facilities "Participation in Metal-Expo helps us maintain our leading position in the market and strengthen relationships with key partners. It’s a great opportunity to showcase our unique solutions and discuss new projects in the metallurgy and engineering sectors," says Stanislav Borovikov, General Director of SalesSolution. In the SalesSolution showroom, visitors will have the opportunity to explore the company’s product range, receive expert consultations, view material and equipment samples, and discuss delivery terms and pricing. In addition to Metal-Expo, the company continues its active involvement in major international industry events. Already in early November, SalesSolution will participate for the fifth time in ADIPEC 2024 in Abu Dhabi — one of the largest conferences in the global oil and gas industry.
More